How do AC drives work?
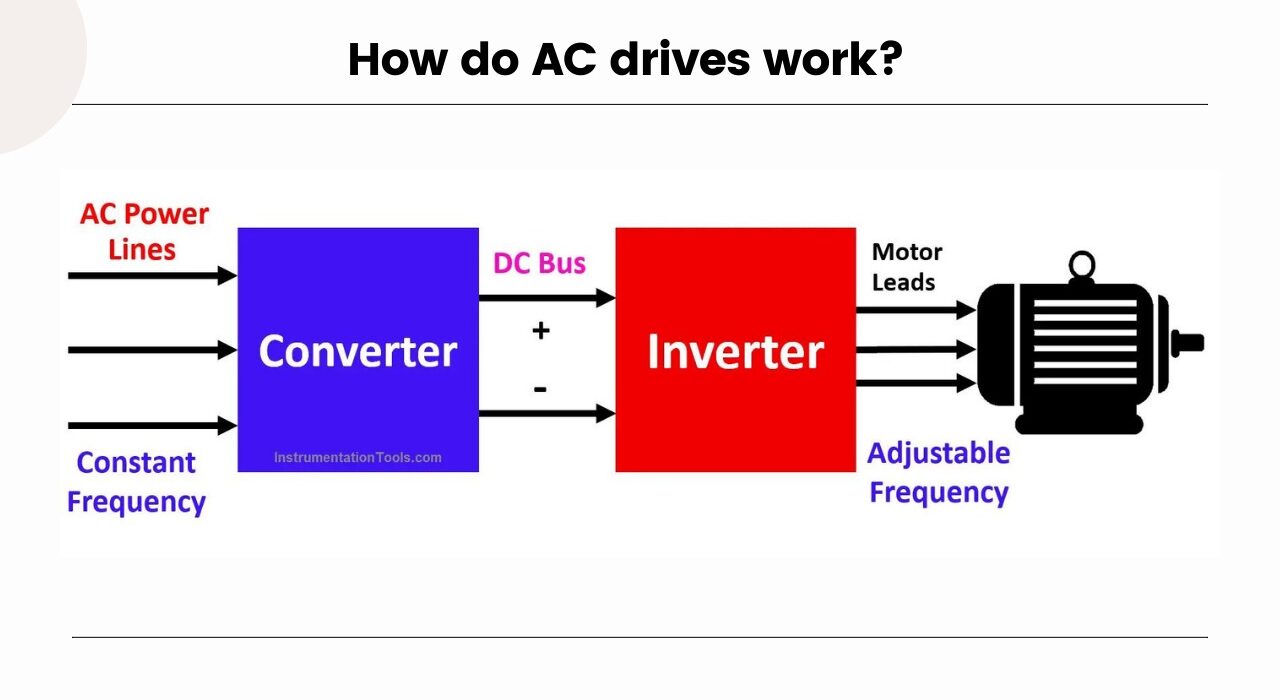
AC drives are essential for regulating the torque, speed, and energy efficiency of AC electric motors. They are crucial components in a variety of industrial applications because of their capabilities for precise motor control, energy conservation, motor protection, and smooth interaction with control and automation systems.
Power Conversion:
Using a rectifier circuit, Allen Bradley AC drives transform the incoming AC power supply from the mains into a DC voltage. To convert AC power into a steady DC voltage, the rectifier circuit commonly uses diodes.
- Rectification: Rectification is the initial phase of power conversion in an AC drive. The entering AC power source is typically at a fixed frequency (such as 50 or 60 Hz), and is converted into a DC voltage by an AC drive using a rectifier circuit. The rectifier circuit efficiently transforms the AC voltage into a pulsing DC voltage by using diodes or other solid-state devices that let current to flow in only one direction.
- DC Bus: Capacitors are used to filter and smooth out the rectified DC voltage, resulting in the DC bus, a reliable DC voltage source. The DC voltage is stored and supplied to the following stages of the AC drive by the capacitors in the DC bus.
DC Bus:
A steady DC voltage source is produced by smoothing out the converted DC voltage and storing it in a DC bus capacitor.
A stable DC voltage is produced after the entering AC power supply has been rectified and filtered. The DC bus is then created by storing this DC voltage in a capacitor bank. Within the AC drive, the DC bus serves as a supplemental energy storage system.
The DC bus’s main function is to give the following stages of the AC drive a reliable and consistent source of DC voltage. Between the rectification stage and the inverter stage, it serves as a buffer.
The inverter stage is powered by the DC voltage that is kept in reserve in the DC bus. This DC voltage is provided to the inverter, which transforms it into an adjustable-frequency and adjustable-voltage AC output for the AC motor. The DC bus makes sure that the inverter stage receives a steady supply of voltage so that it can carry out its conversion.
Check :- Rockwell Automation PowerFlex 4M AC Drive
Inverter Stage:
In an inverter stage, the DC voltage from the DC bus is fed. In order to produce a pulsed waveform, the inverter uses power electronic switches such insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), which quickly turn on and off.
- DC Input: The DC bus, which is normally a steady and smoothed-out DC voltage generated from the rectification stage, feeds the inverter stage with the DC voltage.
- Power Switches: Power electronic switches, such as insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), are used in the inverter stage to regulate the current and voltage going to the motor. The output waveform can be precisely controlled by quickly turning on and off these switches.
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM):
The output voltage and frequency of the inverter are controlled using pulse width modulation techniques. The inverter alters the effective voltage and frequency given to the motor by changing the pulse width and timing.
- Reference Signal: The reference signal produced by the AC drive’s control system denotes the intended voltage or frequency for the motor.
- Carrier Signal: The AC drive creates a signal with a high-frequency carrier. Usually, the fixed frequency of this carrier signal is significantly higher than the required output frequency.
- Modulation: The control system contrasts the carrier signal and reference signal. This comparison establishes the width (duty cycle) of the carrier signal pulses that must be altered in order to match the reference signal.
- PWM Signal Generation: By switching the power electronic switches on and off in accordance with the established duty cycle, the control system produces a PWM signal. If the reference signal value is higher, the switches are switched on during the high portion of the carrier signal, and if the reference signal value is lower, they are turned off during the low portion.
Output to Motor:
The AC motor is connected to the inverter’s modulated AC output. A variable-frequency and variable-voltage supply is given to the motor, allowing for fine control of its speed and torque.
- Variable-Frequency Output: The AC drive’s inverter stage produces an AC output voltage with a variable frequency. The control system normally chooses the output waveform’s frequency based on the motor’s desired speed. The AC drive may regulate the motor’s rotational speed by changing the frequency.
Control System:
The control system for the AC drive keeps track of a number of variables, including motor speed, torque, voltage, and current. To maintain the required motor performance, the inverter’s output is modified using data from sensors or algorithms. To fulfil the needs of the application, the control system can be configured using specific control logic and algorithms.
AC drives offer fine control over the motor’s speed and torque by altering the frequency and voltage of the output delivered to the motor. The control system continuously checks the output and modifies it in accordance with the intended operating parameters to ensure dependable and efficient motor performance.